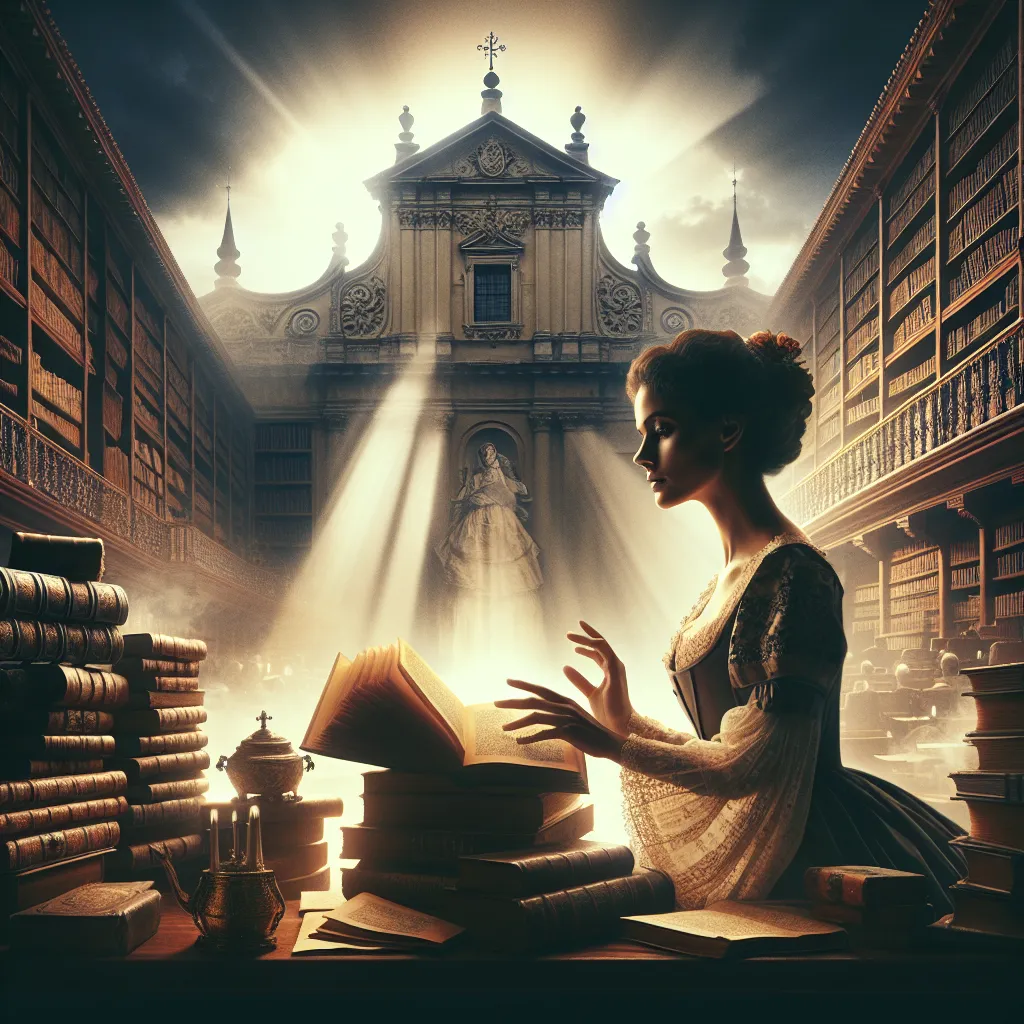
Juana Ramírez de Asbaje sat in front of some of the brightest minds of her time, ready to face their toughest questions. She was invited by the viceroy of New Spain to prove her intelligence. Juana answered every complex query, from difficult math problems to deep philosophical questions, with ease. People compared it to a grand ship defending itself against small boats.
Juana was born in the mid-17th century, when Mexico was under Spanish rule and society was highly stratified. Her maternal grandparents were from Spain, placing them in the upper class. But Juana’s father, a Spanish military captain, left her mother, Doña Isabel, to raise her and her sisters alone. Luckily, her grandfather’s modest wealth provided them a comfortable life. Doña Isabel was a strong woman who managed one of her father’s estates, despite being illiterate and facing societal misogyny. This may have inspired Juana’s confidence.
At age three, Juana secretly followed her older sister to school. She later discovered that higher education was only for men and asked her mother to let her attend school dressed as a boy. When her request was denied, she turned to her grandfather’s private library. By her early teens, she was already skilled in philosophical debate, fluent in Latin, and knowledgeable in the Aztec language Nahuatl.
Juana’s brilliance caught the attention of the royal court in Mexico City, and at sixteen, she became a lady-in-waiting for the viceroy and his wife. Her plays and poems were both admired and controversial. Her famous poem “Foolish Men” criticized sexist double standards, blaming men for corrupting women and then holding them responsible for immorality. Despite the controversy, she was beloved and received numerous marriage proposals, though she was more devoted to knowledge.
In a society dominated by patriarchy, there was only one sanctuary for her: the Church. At twenty, she joined the Hieronymite Convent of Santa Paula and took the name Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz. Sor Juana became a treasured intellect in the church. She wrote dramas, comedies, philosophical and mathematical treatises, and religious music and poetry. She amassed a vast library and was visited by many prominent scholars. As the convent’s treasurer and archivist, she also protected her niece and sisters from exploitation.
However, her outspoken nature led to conflict. In 1690, a bishop published her private critique of a respected sermon, urging her to focus on prayer rather than debate. Sor Juana replied that God gave women intellect to use it. This drew the ire of the conservative Archbishop of Mexico. Gradually, Sor Juana lost her prestige, was forced to sell her books, and cease writing. Furious but unable to leave the church, she renewed her vows and signed them in her own blood as “I, the worst of all.”
Deprived of her scholarly pursuits, Sor Juana devoted herself to charity work. She died in 1695 from an illness contracted while caring for her sisters. Today, Sor Juana is celebrated as the first feminist of the Americas. She is featured in documentaries, novels, operas, and even on Mexico’s 200-peso note. Nobel laureate Octavio Paz once said that Sor Juana’s work is not just a product of history; history itself is shaped by her work.