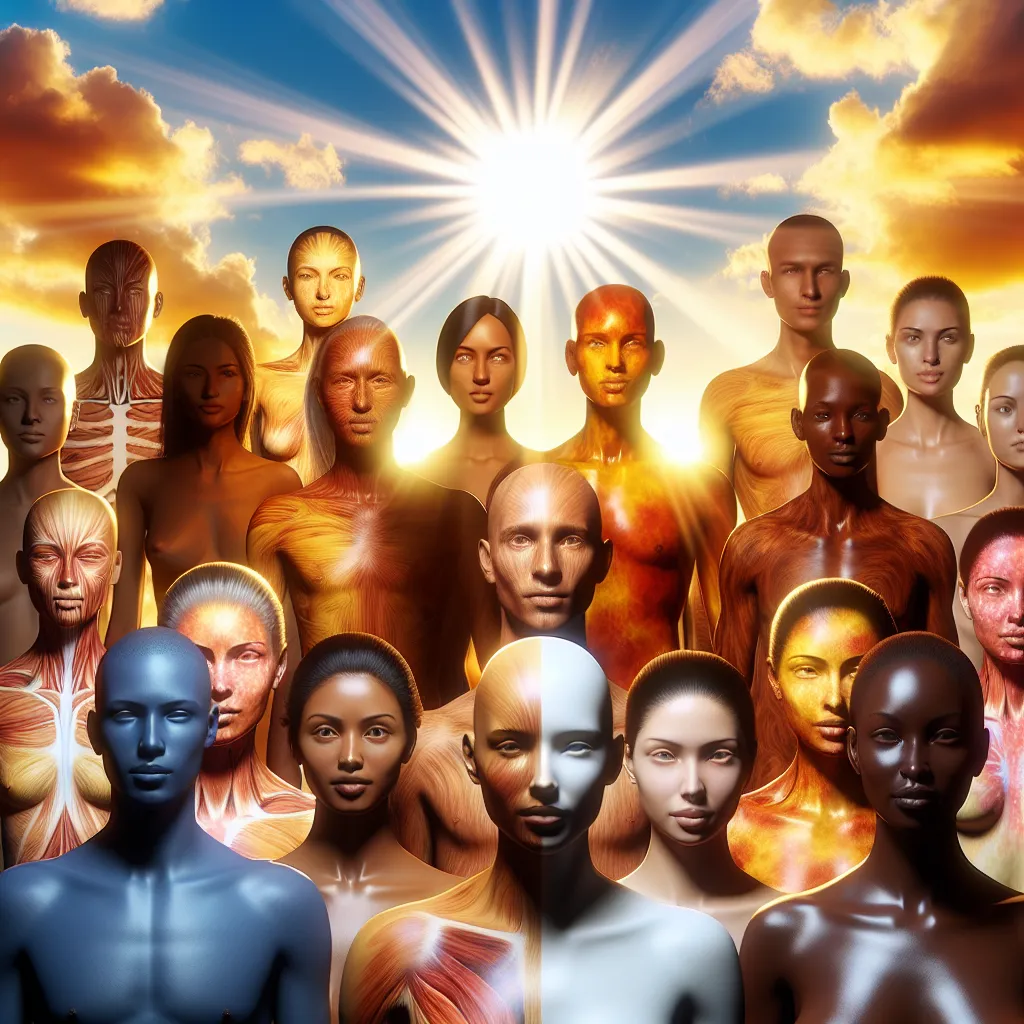
When ultraviolet (UV) sunlight hits our skin, it impacts us differently based on our skin color. Some people turn pink within minutes, while others need hours to see any change. This variation tells a fascinating story of human adaptability and biology, mainly revolving around melanin, the pigment responsible for our skin and hair color. Melanin is produced by skin cells called melanocytes and comes in two types: eumelanin, which gives brown skin tones and black, brown, or blond hair, and pheomelanin, which is behind the reddish browns of freckles and red hair.
Our diverse skin tones are the result of thousands of years of evolution driven by the Sun. About 50,000 years ago, as humans migrated from Africa to Europe and Asia, they experienced greatly varying sun exposure. Those living near the Equator, where UV light is intense, needed to protect themselves from the damaging effects of prolonged UV exposure, which can cause melanoma, a deadly skin cancer.
Although sunscreen didn’t exist 50,000 years ago, our ancestors had a natural defense: melanin. When skin is exposed to UV rays, it triggers light-sensitive receptors called rhodopsin to boost melanin production. This acts as a shield against cell damage. People with darker skin, who have high melanin production and more eumelanin, developed this built-in sunscreen, protecting them from melanoma.
However, when some of these sun-adapted humans migrated north, they faced less intense sunlight. This created a problem because UV light, despite its risks, is crucial for vitamin D synthesis, which strengthens bones and helps absorb minerals like calcium, iron, and magnesium. Dark skin, which blocked much of the UV light, became a disadvantage in lower sunlight regions, leading to vitamin D deficiency and conditions like rickets.
But people with less melanin, whose skin allowed more UV light absorption, produced enough vitamin D to stay healthy. Over thousands of years, natural selection led to lighter skin tones in these regions. Consequently, today we see a wide range of skin colors worldwide: darker, eumelanin-rich skin near the Equator and lighter, pheomelanin-rich skin further from the Sun’s intense rays.
Thus, skin color is an adaptive trait, honed by our ancestors to thrive on a planet bathed in varying levels of sunlight. It reflects our journey and adaptability rather than character.