Epochs & Echoes
Epochs and Echoes: Discover insights on history, finance, politics, and lifestyle with engaging articles that connect past and present.
Check Us OutLatest Posts
Sovereign Wealth Funds: How $11.3 Trillion is Reshaping Global Finance
Sovereign wealth funds (SWFs) are powerful government-owned investment entities reshaping global finance. With assets of $11.3 trillion, they influence markets, drive economic diversification, and support sustainability. SWFs invest globally, impacting asset prices and capital flows. Their growth, especially in commodity-rich nations, presents opportunities and challenges, balancing financial returns with national goals and transparency concerns.
Glowing Bacteria: The Tiny Heroes Revolutionizing Medicine and Saving Lives
Bioluminescent bacteria are revolutionizing medical science. These light-producing microorganisms are used to detect diseases, guide surgeries, and deliver targeted therapies. Scientists engineer them for tracking infections, cancer research, and drug discovery. They also serve as biosensors for biological changes and contamination detection. This interdisciplinary field is advancing healthcare and inspiring innovative research across multiple scientific domains.

Nowruz: Ancient Persian New Year Ritual Blends Tradition and Renewal
Nowruz, the Persian New Year, celebrates spring's arrival with ancient Zoroastrian roots. It features the haft-sīn table, house cleaning, and bonfire jumping. Lasting 13 days, it includes family visits and outdoor festivals. Nowruz spans Central and Western Asia, symbolizing cultural identity and renewal. It blends tradition with modern practices, connecting people to nature and their heritage.

Sovereign Green Bonds: How Governments Are Funding a Sustainable Future
Sovereign green bonds are government-issued debt instruments for funding eco-friendly projects. They signal commitment to sustainability, attract investors, and reshape environmental policies. These bonds follow strict guidelines, ensuring transparency and accountability. The global market has grown significantly, with countries like India and France leading the way. This innovative tool bridges finance and sustainability, transforming how nations fund their green initiatives.
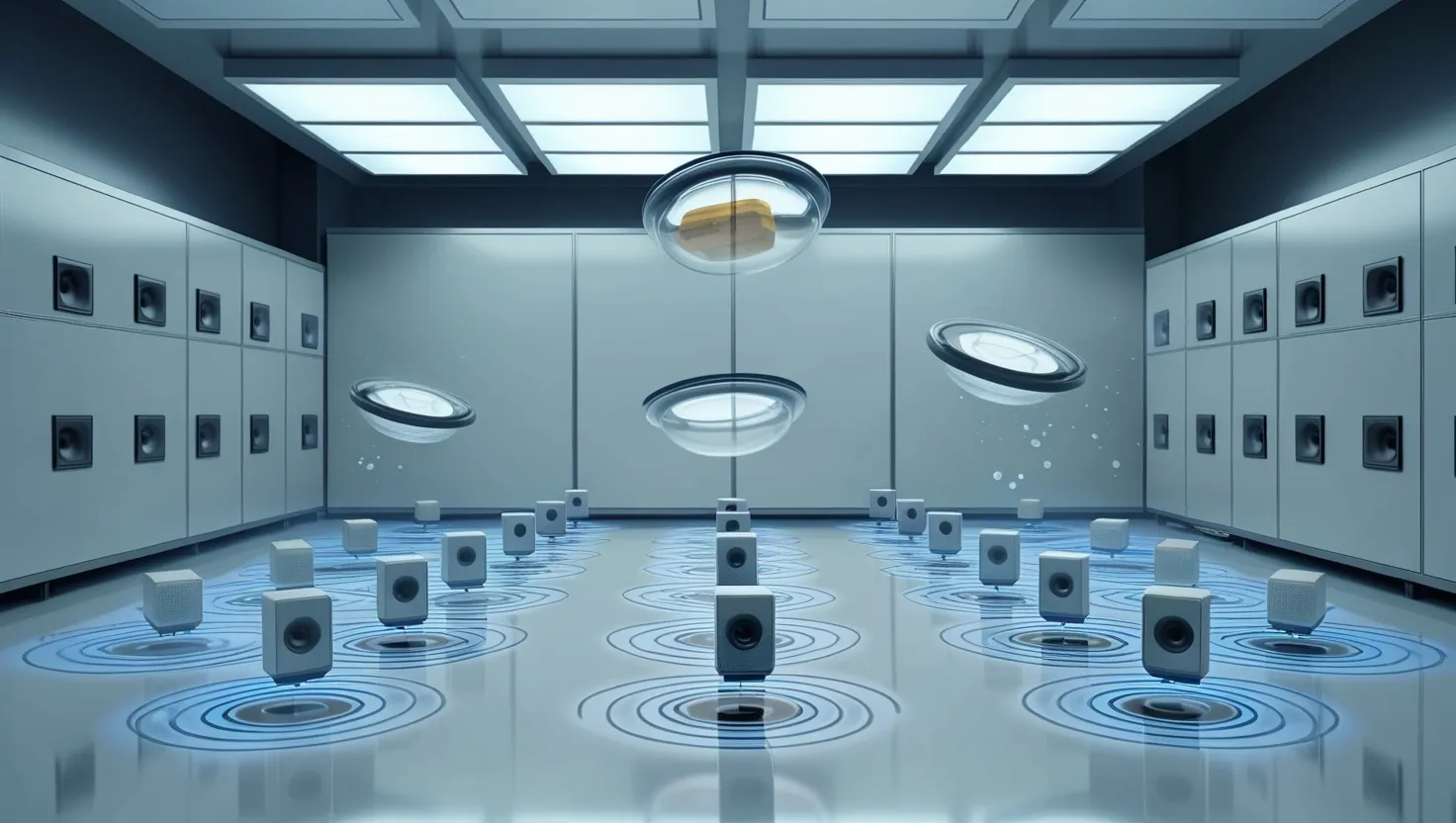

Floating Objects with Sound: The Mind-Blowing Science of Acoustic Levitation
Acoustic levitation uses sound waves to suspend objects in mid-air. It creates a pressure field that counteracts gravity using ultrasound frequencies. This technology has applications in manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, space exploration, and 3D printing. It allows for contactless handling of delicate materials and precise manipulation in zero-gravity environments. While challenging to set up, acoustic levitation shows promise for future innovations in various fields.
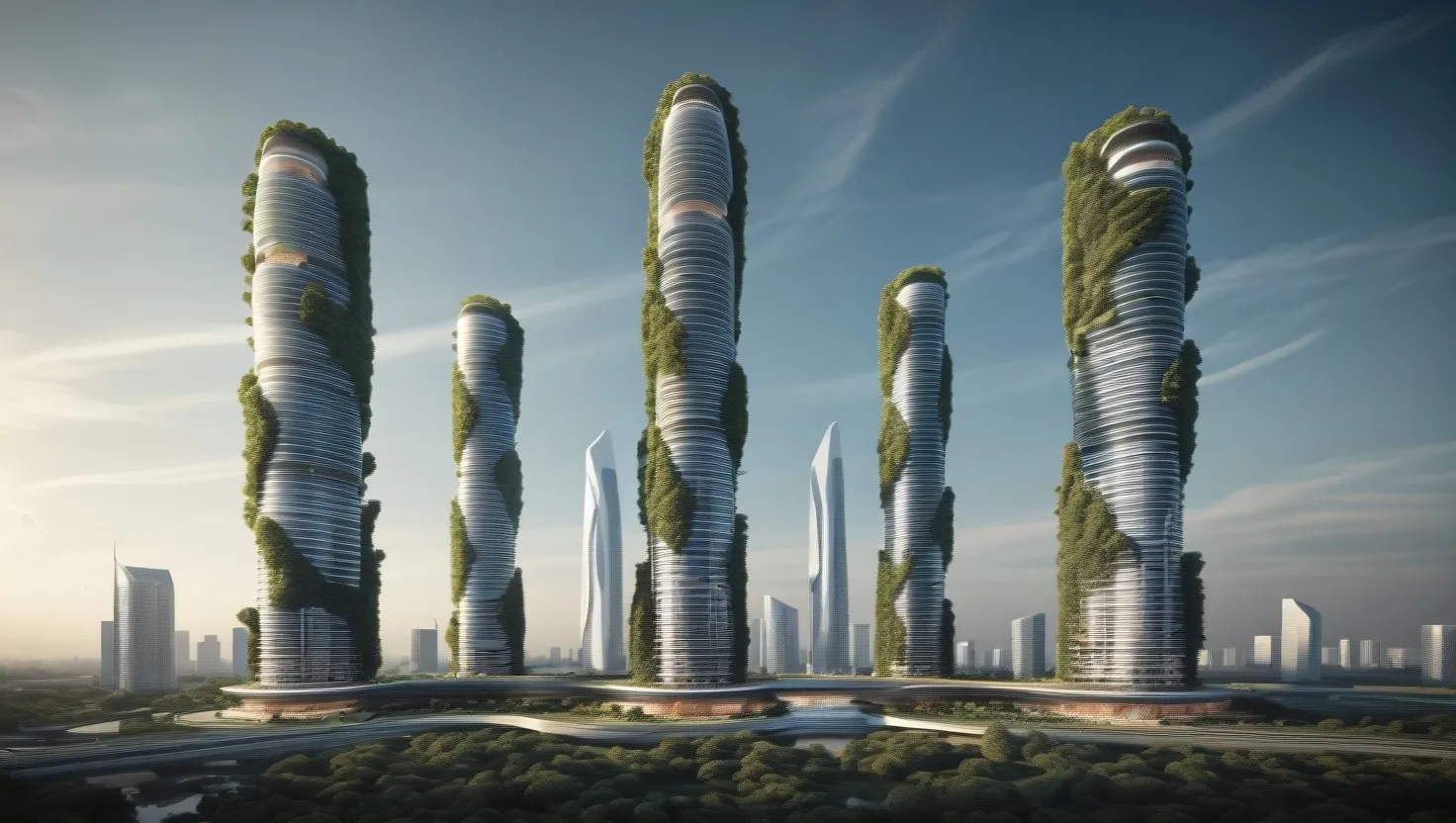

Nature's Blueprint: Incredible Buildings Inspired by Biological Marvels
Biomimetic architecture draws inspiration from nature to create sustainable buildings. Examples include Zimbabwe's Eastgate Centre (termite mounds), Beijing's Bird's Nest (bird nests), and Sydney's One Central Park (vertical gardens). These designs mimic natural structures and processes, resulting in energy-efficient, environmentally friendly buildings that enhance human well-being while reducing environmental impact.
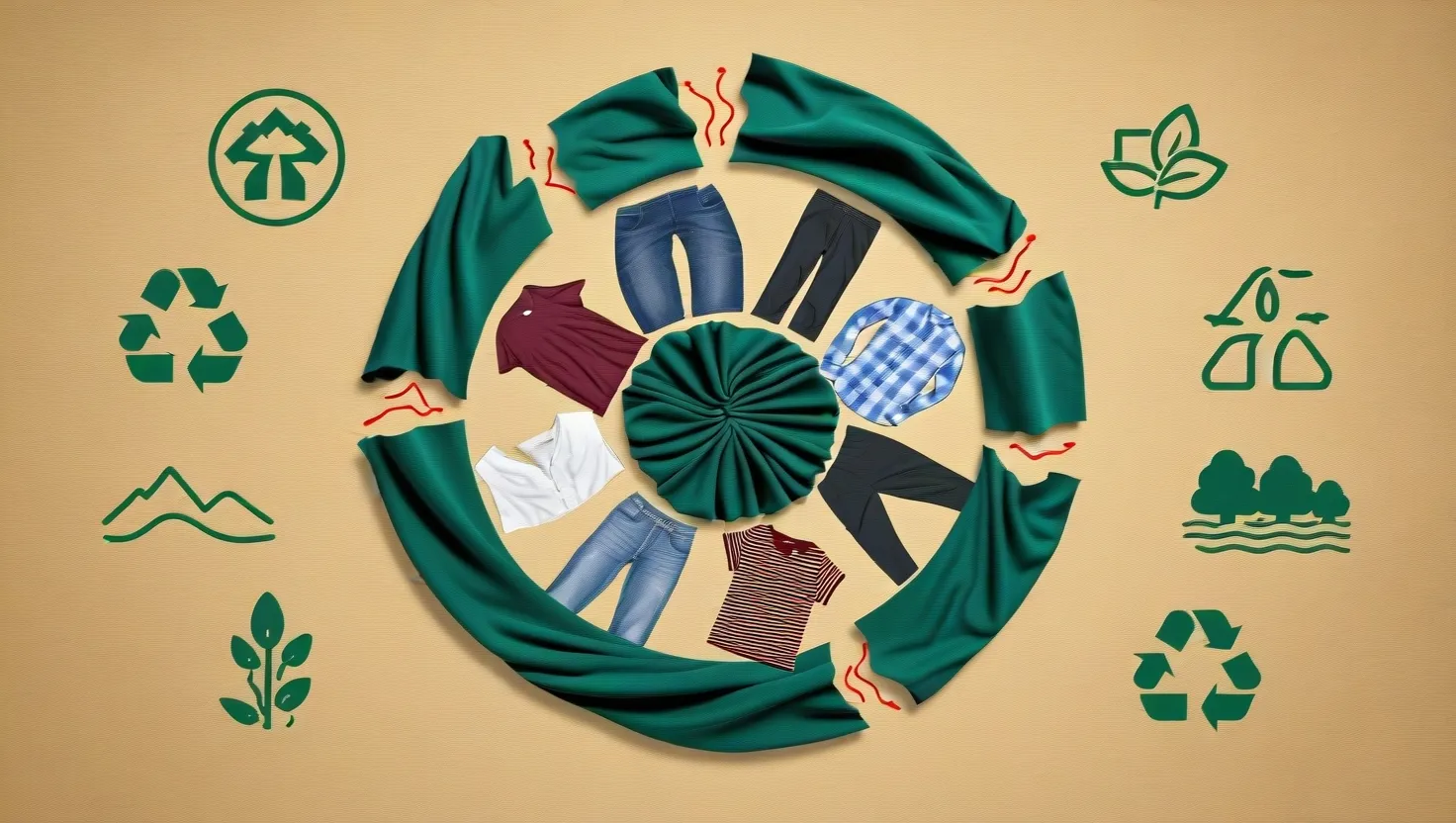

Circular Fashion Revolution: Sustainability Meets Style in Eco-Friendly Clothing Trends
Circular fashion is reshaping the industry by creating a closed-loop system that maximizes resource efficiency and minimizes waste. It focuses on designing durable, timeless garments, using sustainable materials, and promoting recycling and upcycling. This approach reduces environmental impact, meets growing consumer demand for eco-friendly products, and offers long-term cost savings for businesses.
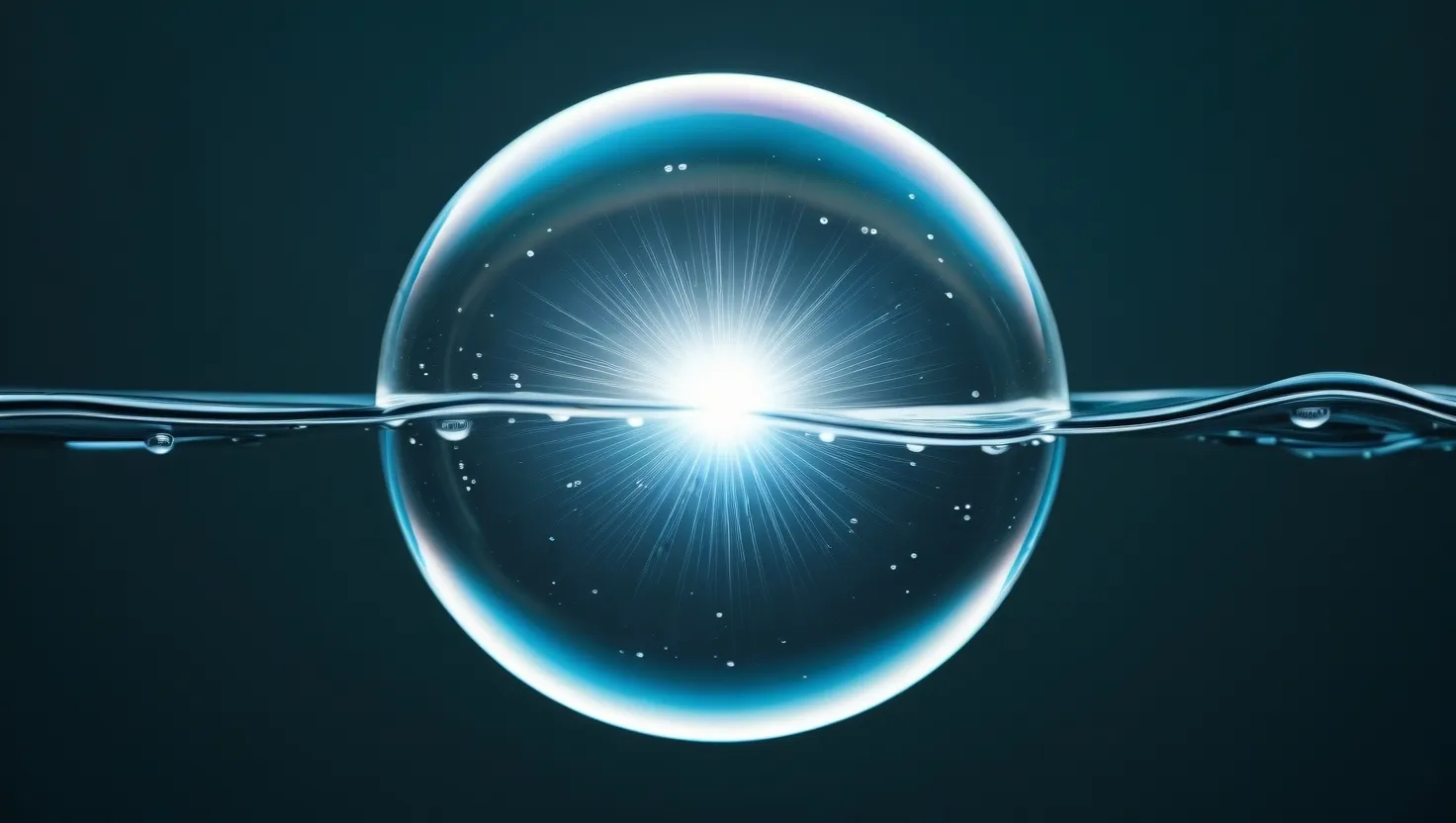

Sound to Light: Tiny Bubbles Create Sun-Hot Flashes in Water
Sonoluminescence: Sound waves create tiny bubbles that emit brief, intense light flashes. This phenomenon involves extreme temperatures and pressures within collapsing bubbles, producing ultraviolet light in picoseconds. While the exact mechanism remains debated, it has potential applications in medical imaging and energy production. This intriguing process challenges our understanding of fundamental physics and energy conversion.

Baháʼí Fast: 19 Days of Spiritual Growth That Will Change Your Life
The Baháʼí Nineteen-Day Fast is a spiritual practice of abstaining from food and drink from sunrise to sunset for 19 days in March. It's a time for reflection, prayer, and spiritual growth. This fast emphasizes self-discipline, community unity, and inner renewal. It concludes with Naw-Rúz, the Baháʼí New Year celebration, marking spiritual rebirth.

Molecular Gastronomy: Science Meets Cuisine in Mind-Blowing Culinary Creations
Molecular gastronomy blends science and cooking, exploring food's physical and chemical changes. Chefs use lab tools to create innovative dishes, manipulating ingredients at a molecular level for new textures and flavors. It involves unconventional ingredients like liquid nitrogen and hydrocolloids. This approach enhances dining experiences, engaging all senses and influencing the food industry's approach to taste and nutrition.

Synesthesia: When Colors Have Taste and Numbers Have Hues
Synesthesia: A neurological condition where senses blend, creating unique perceptions. Common types include seeing colors for letters or tasting words. It's genetic, not a disorder, and often enhances creativity. Synesthetes have more brain connections between sensory areas. This phenomenon offers insights into human perception and brain function, challenging traditional views on sensory processing.

Sealand: The Tiny Sea Fort That Declared Itself a Country
Sealand, a tiny micronation in the North Sea, was founded in 1967 on a former WWII sea fort. Despite its small size, it has a constitution, government, flag, and currency. Sealand's history includes legal battles, a coup attempt, and economic ventures. While unrecognized by other nations, it raises questions about sovereignty and statehood in the modern world.
Aral Sea's Rebirth: How Science and Cooperation Are Reviving a Lost Wonder
The Aral Sea's decline due to Soviet-era irrigation projects led to ecological disaster. Restoration efforts, led by Kazakhstan, include the Kok-Aral Dam, which revived the Northern Aral Sea. Innovative techniques like satellite monitoring and saxaul plantations combat environmental damage. Water management, climate adaptation, and international cooperation are key. These efforts offer hope and lessons for global environmental challenges.
