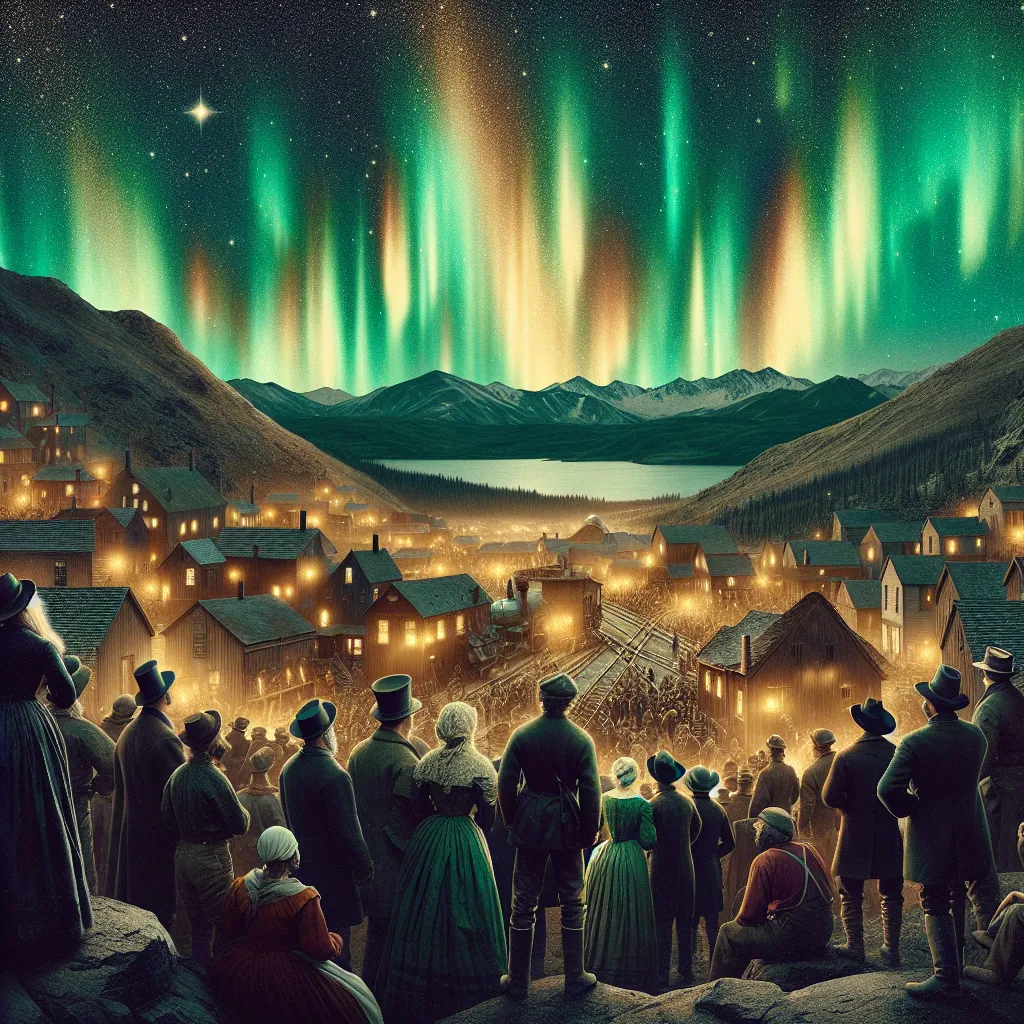
On a seemingly typical morning on September 1st, 1859, miners in Colorado dull with gold fever were startled to find the sky ablaze. Astonishingly, it wasn’t dawn but 1 a.m., and the dazzling lights weren’t from the Sun but a magnificent aurora visible as far as the Caribbean. This spectacle, causing many to worry about massive city fires, was actually the result of the largest recorded solar storm, now known as the Carrington Event.
Solar storms are due to magnetic fields, crafted by moving electrically charged particles like protons and electrons. Earth’s magnetic field, for instance, forms from molten metals in its outer core. Similarly, the Sun’s magnetic field arises from plasma movements within it. These movements generate sunspots - areas of intense magnetic activity. When these magnetic fields twist excessively, they snap, releasing energy and launching plasma into space in events called coronal mass ejections. This plasma, primarily protons and electrons, can traverse the distance from the Sun to Earth in just days.
When these ejections hit Earth, they follow its magnetic field lines, exciting atoms in the atmosphere like oxygen and nitrogen. This excitement releases photons, creating the breathtaking auroras normally seen near the poles. However, powerful solar storms can light up much larger areas of the sky.
Despite their beauty, solar storms pose significant risks to our technology. High-energy particles from these storms generate secondary magnetic fields, which can cause rogue currents, leading to electrical equipment failures. The Carrington Event only managed to affect telegraph systems, but today’s technology is far more vulnerable. In 1921, a strong storm wrecked telegraph and telephone systems and ignited fires in New York’s railway control building. Weaker storms in 1989 and 2003 led to power outages in Canada and damaged satellites.
A Carrington-level event today could wreak havoc on our power-dependent world. Thankfully, we’re not entirely at the mercy of the Sun. Scientists understand the Sun’s 11-year cycle of magnetic activity, helping predict when solar storms might strike. Improved space weather forecasts and mitigation measures, like preemptive power grid shutdowns and special shielding for satellites, offer some protection. Yet, despite these efforts, the next major solar storm’s impact on our technology remains uncertain.
One thing is clear: should that day come, the shimmering auroras may be the only lights guiding our way forward.